When pain or discomfort occurs when lying or sitting, our brain sends out warning signals that we should move. By regularly changing position in bed, chair or wheelchair, the risk of pressure injuries can be reduced. For people with reduced sensation or mobility, this can be difficult to do on their own, and they may need help reducing pressure on sensitive areas through repositioning and positioning (1).

Changing position
Why is position change important?
Positioning and repositioning are done to reduce pressure and minimize the time sensitive areas of the body are exposed to pressure. Care recipients may need to change position to lie or sit more comfortably, or to facilitate personal hygiene (2).


What should I consider during repositioning?
Determine the frequency and number of repositioning based on the care recipient’s activity and mobility level, skin condition, and overall health. A repositioning disk can be used as a reminder for the next repositioning (3).
Use a repositioning schedule to describe the frequency, time, and specific positions for repositioning. Adapt lying and sitting positions to minimize pressure on the skin and bony prominences. The length of time a care recipient can sit or lie without repositioning varies individually. Keep in mind that high pressure over a short period and low pressure over a long period can be equally harmful. A good guideline is to avoid more than 2 hours between repositioning (3).
Remember! Repositioning is crucial regardless of the type of pressure redistribution or pressure-relieving surface being used (3).
How do I position a person with, or at risk for, pressure ulcers?
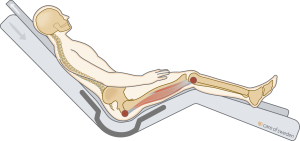
Positioning cushions can be used to relieve pressure and position the care recipient based on their diagnosis, needs, and overall health. Ensure that the pressure relief is as even as possible and remember that repositioning will always exert increased pressure on another body part (3).
Instruction videos
In our positioning videos, we provide you with tips on how you can use Care of Sweden’s positioning cushions in several different ways.
References
(1) Lindholm, C. (2018). Sår (4 uppl). Studentlitteratur
(2) Vårdhandboken. Åtgärder för att förebygga. https://www.vardhandboken.se/vard-och-behandling/hud-och-sar/trycksar/atgarder-for-att-forebygga/ Retrieved 2022-10-17
(3) European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel, National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel and Pan Pacific Pressure Injury Alliance. Prevention and Treatment of Pressure Ulcers/Injuries: Clinical Practice Guideline. The international Guideline. Emily Haesler (Ed.). EPUAP/NPIAP/PPPIA: 2019
